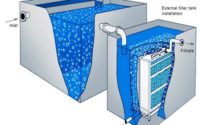
Nutrient Recovery Systems: A boon in Wastewater Management
Nutrient Recovery Systems are designed and manufactured to recover nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater streams and transform the recovered resources into an eco-friendly fertilizer fit for agricultural applications. The nutrient recovery systems are tailored to clean the effluent by extracting and converting nutrients into a highly efficient and reusable feedstock. Owing to urging need to mitigate challenges such as climate change, increasing population, food security issues, deteriorating water quality and water scarcity, the demand for nutrient recovery systems is witnessing an inclining trend. Moreover, the stringent nitrogen and phosphorus discharge limits laid by government agencies would further escalate the Global Nutrient Recovery Systems Market through 2026.
How are the Nutrient Recovery Systems, a solution to growing Wastewater problem?
The wastewater is one of the major causative agent for increasing eutrophication and rising algal boom in natural waterbodies. Presence of excess nutrients in lakes and rivers deteriorate the water quality, thereby negatively impacting the tourism industry, demanding tremendous expenditure on wastewater treatment technologies and equipment.
With the aid of nutrient recovery systems, the wastewater treatment and disposal is witnessing a shift towards reuse, recycle and resource recovery. The nutrient recovery systems are largely tailored to utilize waste streams generated by animal feeding operations, crop farming, septic systems, storm water, livestock, industrial and municipal systems as reliable alternative source of water and recover essential nutrients for agricultural purposes.
World Total Demand for Fertilizer Nutrient Use, 2015-2020F (Thousand Tons)
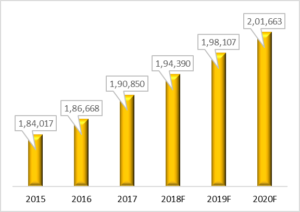
With the phosphorus being a finite resource, it is estimated that the demand for Phosphorus would outpace its supply in the future. As a result, the concept of recovering nutrients from wastewater through nutrient recovery systems is gaining recognition worldwide. In addition to the contribution of wastewater as an economic and sustainable source of energy, nutrients and other useful by-products, the nutrient recovery process is also providing a potential business opportunity to municipalities as an additional revenue stream through sales of recovered NPK fertilizers.
Technological Progress in Nutrient Recovery:
Enhanced Carbon Management: The second-generation nutrient recovery systems feature operational benefits such as improvised biodegradation and higher biogas yield, thereby exhibiting increased resource recovery rates. Moreover, the lower OPEX is further driving the adoption of nutrient recovery systems.
Request for Sample Report Today!
Zero Waste Approach: Industrial researchers are constantly experimenting to achieve zero waste production at the end of nutrient recovery process. For instance, the chemical company Budenheim has come up with the EXTRAPHOS process, wherein the phosphorus is recovered as a commercial product called Dicalciumphosphate (DCP) from sewage sludge using pressurized carbon dioxide, which is later recycled internally. The zero-waste approach adopted by the company is reflecting a growing trend for the nutrient recovery industry.
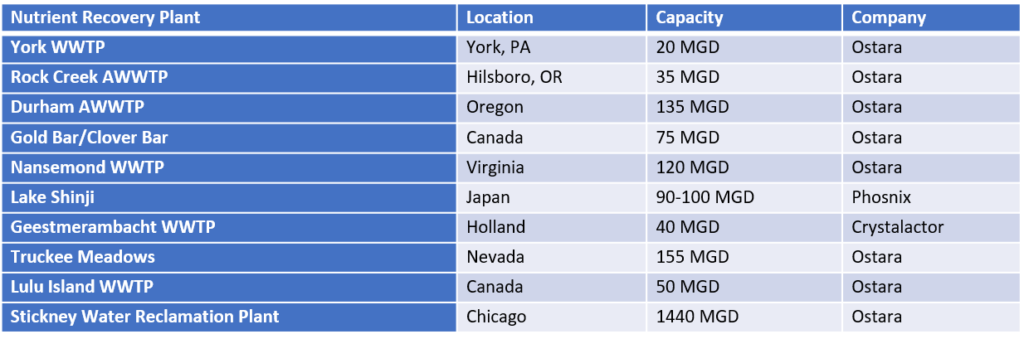
Partial List of Nutrient Recovery Plants, As of 2016
Favorable Regulations and Directives:
Europe: The European Commission’s circular economy package 2015, led certain revisions to the existing fertilizer regulation (2003/2003/EC) which are in line with the focus on nutrient recovery processes and systems. The strategic alliance between the European Commission’s Directorate-General for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs (DG GROW) and the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission (DG JRC) is primarily aimed at the development of possible process and product criteria for struvite, biochar and ash-based products for usage in fertilizers.
- Netherlands: In June 2016, the ARREAU action group of European Innovation Partnerships (EIP) launched a Struvite Recovery & Recycling Learning Alliance (SRRLA) in Amersfoort.
- Switzerland: In January 2016, the country enforced a new waste regulation, mandating phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge and meat & bone meal within a ten-year transition phase.
- Germany: The country has finalized the draft of the sewage sludge ordinance, mandating phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge for German wastewater treatment plants greater than 50,000 PE. The ordinance is expected to come into force by the beginning of 2018.
North America: The US EPA is increasingly focusing on recycling resources for effective utilization in farming practices. As a result, the organization is undertaking several efforts and steps to:
- Develop novel technologies to stimulate nutrient recovery for nitrogen and phosphorus in water systems.
- Demonstrate varied nutrient recovery options to test, validate, assess, evaluate and better understanding of recovery technologies.
Conclusion: In conclusion, Global Nutrient Recovery Systems market is projected to exhibit rapid growth over the coming years owing to the strict government regulations on discharge of Nitrogen or Phosphorus into the water bodies. The nutrient recovery systems are increasingly adopted as a preferred option over conventional systems due to operational and economic benefits along with lower environmental impact. With shifting global paradigm towards circular economy, the recovery of major macronutrients such as N, P and K from wastewater is acting as an additional revenue stream for municipalities around the globe, wherein they assist agribusiness with required nutrients for farming. Consequently, different commercial end products (Struvite fertilizer, Calcium‐phosphate, Magnesium‐phosphate, etc.) obtained along with treated water is emanating huge growth opportunities for nutrient recovery systems across the globe.