The Art and Science of Mixed Waste Plastic Recycling: A Sustainable Odyssey
Plastic waste (PW) has been one of the world’s biggest pollution problems in recent years. It has been estimated that the world produces 300 million tons of plastics annually, and only a small percentage of this amount is recycled. Only a fraction of our plastic waste is recycled, while the production of new plastic, derived from fossil fuels, keeps rising. This alarming scenario has compelled scientists to explore fresh approaches to longstanding recycling challenges, such as the complexity of recycling mixed plastics. Yet, they have encountered a significant chemical obstacle: when different plastics are melted together, their distinct monomers tend to separate, much like oil and water. Mixed plastic waste, in particular, poses a significant challenge due to its complexity and lack of market demands. However, there are many groundbreaking initiatives across the globe, aiming to tackle the challenge of mixed waste plastic recycling. This blog post delves into the art and science behind mixed waste plastic recycling and how it can be a sustainable practice for the future.
Several published reports claim that India recycles 60% of the total PW generated annually which is the highest among other countries such as Germany and Austria with more than 50% recycling.
First and foremost, mixed waste plastic recycling is the process of sorting, cleaning, and processing plastic wastes of different types into new materials. This process can be a long and complicated one, with different technologies and methods being utilized. One such technology is pyrolysis, a method of converting mixed waste plastic into crude oil. This process works by heating the plastic at a high temperature in the absence of oxygen, resulting in a liquid fuel.
Another innovative recycling method used is the mechanical recycling of mixed plastic wastes. This method involves grinding and washing plastic waste into small pieces, which are then melted down to make new products. Mechanical recycling is one of the most widely used methods of recycling plastic and is highly efficient when compared to other methods.
In addition to these methods, advancements in technology have enabled chemical recycling, a method that involves breaking down the plastic’s molecular structure using chemical reactions to make it suitable for reuse. Chemical recycling is still in its infancy stages and requires further research and development.
Mixed waste plastic recycling also involves the use of smart and sophisticated sorting machines. These machines use a combination of X-ray technology, cameras, and sensors to accurately sort different types of plastics based on their chemical composition. This process allows for more efficient and effective recycling, ultimately reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills.
Finally, it’s worth noting that the art of mixed waste plastic recycling is also about recognizing the importance of reducing the overall plastic consumption. By reducing the use of plastics, the amount of waste produced can be decreased, making it easier to recycle and leading to a more sustainable future.
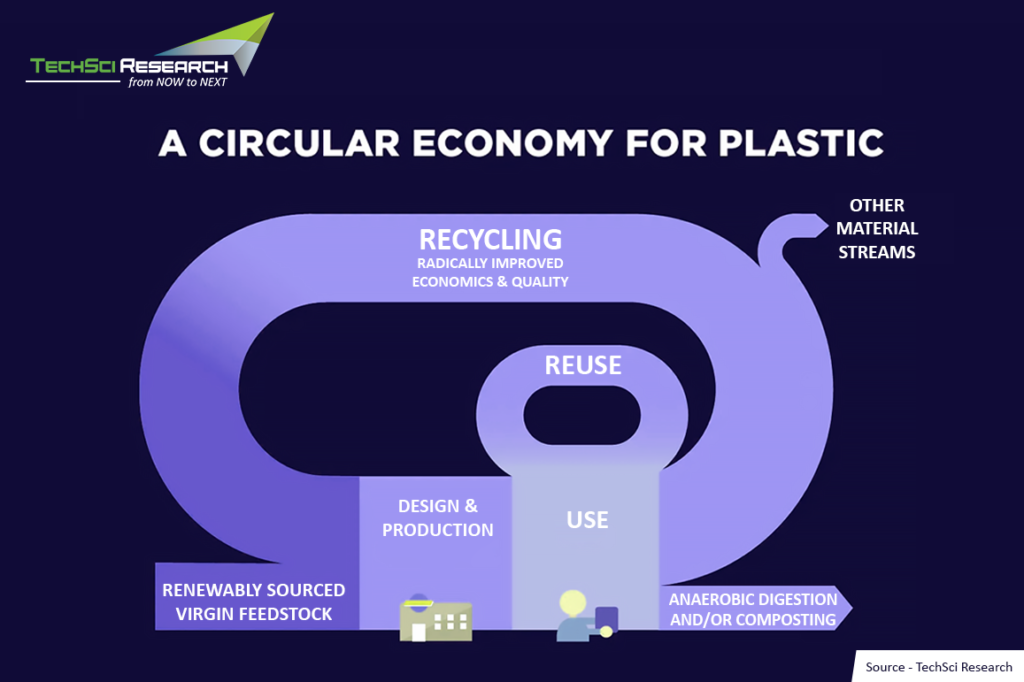
According to the Techsci Research report “Plastic Recycling Market – Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, 2018-2028 Segmented By Type (Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Polystyrene (PS) and Others), By Source (Bottles, Films, Fibers, Foams, and Others), By End-User (Packaging, Building & Construction, Textile, Automotive, Electrical & Electronics, and Others), By Region, and Competition 2018-2028,” the Global Plastic Recycling Market is anticipated to project robust growth through 2028 owing to growing environmental concerns. In 2021, the total consumption of plastic in India amounted to approximately 18 million tonnes. Plastic waste leads to environmental pollution and litter. These can have negative impact on both people and the environment. Recycling plastic involves collecting used plastic waste and turning it into functional plastic items. According to recent studies, if the business continues in usual manner for virgin plastic, 7.7 billion metric tonnes of plastic are expected to be improperly disposed of, burned or released into the environment between now and 2040.
Challenges
1.Sorting Challenges: Sorting mixed plastics is one of the primary challenges of recycling. It requires separating the different types of plastic based on their composition and properties. Due to their various shapes and textures, sorting mixed plastics can be complicated. Manual sorting processes are usually inaccurate and inefficient, resulting in recycled materials of reduced quality. Solutions to this issue include using AI and robotic technology to automate the sorting process, improving accuracy and efficiency.
2. Contamination: Contamination is another significant challenge facing mixed waste plastic recycling. Contamination occurs when other materials, such as paper or food waste, are mixed with plastic. Contaminants decrease the quality of the recycled plastic, rendering it unusable. Efforts to mitigate this challenge include refining waste management strategies to encourage the separation of plastic from other waste materials at the source. Additionally, strict regulations should be enforced to deter individuals from improper disposal of plastic waste.
3. Lack of Market Value: Another struggle of mixed waste plastic recycling is the lack of market value for recycled materials. While virgin plastic is more affordable than recycled plastic, recycled plastic still requires additional processing, transportation, and purification before it can be used. Lack of demand and market value for recycled plastic results in a decreased incentive to recycle. Encouraging demand for recycled plastic is vital to promote the reuse of plastic materials.
4. Limited Infrastructure: Mixed waste plastic recycling shares limited infrastructure with other recycling programs, making it difficult to handle and process the increasing volume of mixed plastics. Building new infrastructure or modifying existing facilities to handle mixed plastic is costly and time-consuming, making it an immense challenge. Collaboration between governments and the private sector is necessary to address this challenge and promote the development of high-volume recycling plants.
5. Consumer Behavior: Consumer behavior is another issue that hinders mixed waste plastic recycling. Many individuals are unaware of the recycling process and its environmental impact; thus, making recycling less of a priority. Encouraging awareness and proper recycling education campaigns, such as designing effective recycling labels, can help modify consumer behavior and promote sustainable practices.
Other than these there are other two main challenges that hinder effective plastic recycling: material variability and the costs associated with sorting and categorizing waste plastics. Plastics are carefully engineered products manufactured under controlled conditions to meet specific specifications and physical properties. These properties are chosen to suit various end-use applications and manufacturing requirements. For instance, polyethylene is produced using different technologies and comes in a range of densities and molecular weights to cater to diverse applications, such as films, bottles, caps, pipes, and biomedical materials. The supply chain for plastics is further complicated by blending, the use of additives, and fillers. Moreover, end users may incorporate their own additives and combine different types of plastics in a single product. As a result, single plastics with known properties and additives are the most suitable for reuse, assuming they can be collected and reprocessed in a cost-effective manner. However, collecting waste plastics can be challenging due to low volumes and material diversity. While it is technically possible to separate mixed plastics into distinct streams, it is currently economically viable only for higher-value plastics like PET or HDPE used in bottles. Therefore, effective recycling relies on understanding the range of properties in the separated materials, having an efficient collection infrastructure, and employing a reprocessing method that produces reusable products.
Recycling mixed waste plastic is a vital component in mitigating the impacts of plastic pollution on the environment. The challenges of mixed plastic recycling are daunting but with the continued efforts of a collaborative team of private entities, governments, and individuals, we can achieve improved and innovative solutions. Sorting technologies, waste management strategies, refining consumer behavior, and educating the public are essential steps to overcoming the problems that arise in mixed plastic recycling.
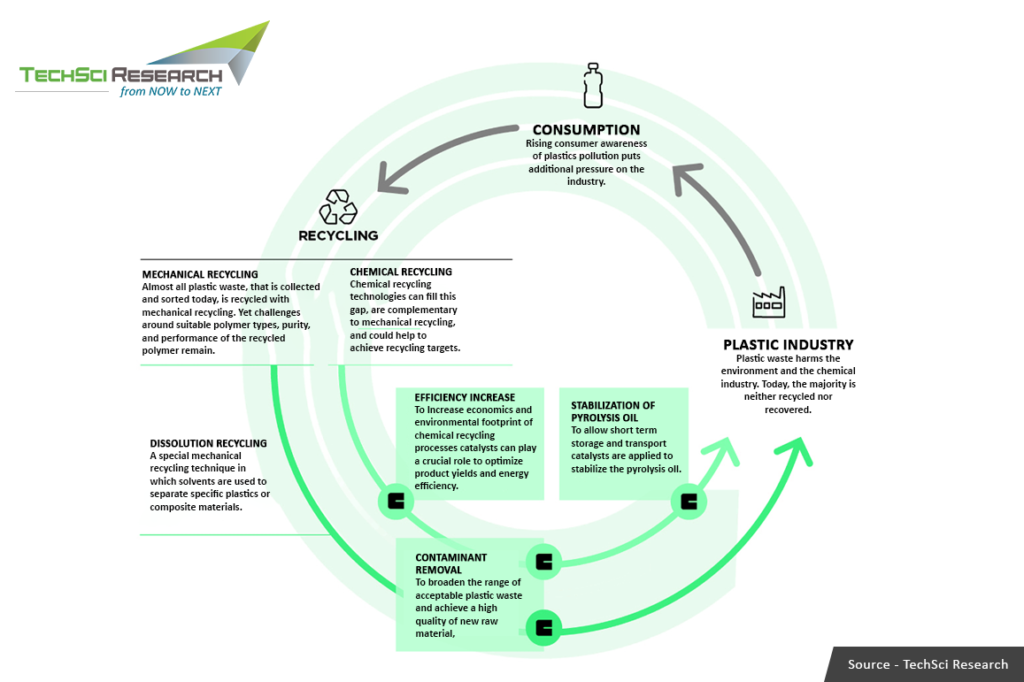
Reuse and Applications of Mixed Plastic Waste
Powder Impression Moulding (PIM) is a process that offers the potential to create a variety of moulded items using low-value and highly diverse plastic blends. UK’s 2K Manufacturing has successfully utilized this process for producing hoarding panels. Encapsulation is another technique where recycled plastic acts as a “former” and is then coated with a thin layer of higher-value plastic. This allows the product to possess the appearance and many performance characteristics of the higher-value encapsulated plastic. Fibre Plastic Composites (FPC) have seen significant growth since the early 1990s in the US and have been effectively developed for specialized applications in Europe. These composites can incorporate a wide range of plastic fibers, from high-value PET with carbon nanotubes to low-value wood and other waste cellulosic fibers combined with mixed polyolefins.
According to the Techsci Research report “Solvent Based Plastic Recycling Market – Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, & Forecast 2018-2028 Segmented By Product (Polyethylene, Polyethylene Terephthalate, Polypropylene, Polyvinyl Chloride, Polystyrene, Others), By Application (Building & Construction, Packaging, Electrical & Electronics, Textiles, Automotive, Others), By Region, Competition,” Global Solvent Based Plastic Recycling Market was valued at USD 623.67 million in 2022 and is likely to grow at a robust rate in the forecast period with a CAGR of 5.35% through 2028. Global plastic crisis has underscored the urgent need for innovative and sustainable solutions in waste management. Solvent Based Plastic Recycling is a sophisticated process which includes the use of solvents to dissolve and separate different types of plastics.
Solvent-based plastic recycling as a process that utilizes solvents to dissolve and separate plastics has witnessed a surge in efficiency and viability owing to the technological advancements. One of the major breakthroughs is the development of advanced separation technologies which can effectively handle a wide range of plastics. Several businesses are adopting stringent sustainability goals which encompass responsible waste management and solvent based plastic recycling due to its ability to provide high-quality recycled resins has become a strategic choice for companies focusing on using recycled materials.
The key market trends include diversification of feedstocks, stringent environmental regulations, and the focus on circular economy.
Top 5 Companies in the Mixed Waste Plastic Recycling Market
ReNew ELP:
ReNew ELP, a British startup, offers a platform for transforming end-of-life plastics into high-grade chemicals and oils. Their innovative process involves the utilization of a patented Catalytic Hydrothermal Reactor, which employs water at supercritical temperatures to generate valuable by-products.
Loop Industries:
Loop Industries, a Canadian startup, has pioneered a patented PET-based plastic depolymerization process. This innovative method effectively separates DMT and MEG from plastic waste, allowing for the creation of new plastic packaging and a significant reduction in plastic pollution. Notably, this process requires lower levels of heat and pressure compared to conventional conversion methods, making it both efficient and environmentally friendly
Brightmark Energy:
Brightmark Energy, a US-based startup, specializes in the conversion of both organic and inorganic waste into valuable renewable resources. The innovative plastic conversion process efficiently recycles various types of plastic into high-quality ultra-low sulfur diesel, naphtha (gasoline), and wax. This scalable solution not only addresses plastic pollution but also supports cities in achieving significant reductions in their environmental impact.
PURA Loop:
PURA Loop, a startup based in Hong Kong, specializes in developing solutions for the treatment and recovery of non-recyclable hazardous industrial sludge and mixed plastics. The company’s cutting-edge technology utilizes microwave-enhanced catalytic pyrolysis to treat the waste at a molecular level. What sets their process apart is that it requires no pre-processing or sorting of waste, resulting in a range of compounds that find applications in various industries.
Novoloop:
Novoloop, a US-based startup, is dedicated to developing Lifecycling, a circular economy solution for plastic waste. Leveraging its innovative ATOD technology, Novoloop effectively converts hard-to-recycle polyethylene into valuable chemical building blocks, boasting a lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels.
These building blocks are further utilized in the production of high-performance materials like TPU. One notable achievement by Novoloop is the creation of a running shoe outsole using Lifecycle TPU derived from plastic waste. This exemplifies how the process transforms discarded materials into valuable new products, showcasing the potential of sustainable innovation.
Conclusion:
Mixed waste plastic recycling is an important step towards a sustainable future, and while it may seem like a daunting challenge, there are innumerable technological advancements and developments being made every day to tackle it. From mechanical recycling to chemical recycling and the use of sophisticated sorting machines, the science behind mixed waste plastic recycling is rapidly progressing. At the same time, an effective approach involves a shift in attitude and behavior towards reducing the plastic consumption. But with a concerted effort by everyone, a lasting impact on the environment can be made, thereby realizing the true potential of mixed waste plastic recycling.