How can Companies Enter Germany?
As the 5th largest economy in the world with an innovative business culture and manufacturing dominance, Germany stands as an enticing destination for companies seeking for international expansion. Germany’s economic policies have been built upon the social market economy principles that combine the benefits of social policies along with the free-market capitalism to ensure a fair balance between social welfare and market competitiveness. The country, with an estimated GDP of USD4319 trillion, accounts for 20% of the entire EU GDP and is projected to grow at 4% in 2022, an increase from 2021’s growth rate of 2.5%.
Why to Choose Germany?
Consistent growth of GDP in entire EU, large consumer market, world-class infrastructure, stable political and economic environment for growth, free market capitalism, skilled workforce combined with the strategic position of Germany in the European Union are some of the factors that can benefit companies planning to enter the country for business growth. Besides, business opportunities in Germany across various end-use industries such as machinery, chemicals, motor industry, metals manufacturing and processing, consumer electronics, aerospace, IT, and construction are immense. Moreover, the economy is relatively open to exports and third-country import duties, restriction, and prohibitions and currently has multiple EU trade agreements with countries like USA.
In terms of ease of doing business, Germany ranks 22nd out of the 190 countries and comes in the 4th and 13th place in resolving insolvency and enforcing contracts respectively, which infers that it’s relatively easy to do business in the country. The country has strong intellectual property (IP) rights, especially in industrial and automotive engineering with a robust copyright, patent law and trademark law.
As the tastes and interests of consumers differ from one German region to another, the market entrants must consider the regional differences and offer innovative products featuring high quality and modern styling to develop a strong national market presence. Price is the main factor for German consumers, but instead quality and reliability. With a reputation for research and innovation, Germany has been successful in attracting global FDI. Currently, there are 45,000 companies from around the world carrying out business operations.
Here is a comprehensive guide for foreign companies seeking to make the transition into the German market, irrespective of the sector.
Choose the Type of Company
Germany ranks 125th on the World’s Bank starting business index as it can take several months to establish a German entity. Besides, foreign companies must also contend to the complex bureaucratic requirements at the local level that includes registering with various agencies. There are three kinds of entities that the companies can establish, namely Sole Proprietorship, Business Partnership, and Corporation. Sole Proprietorship, also referred as Gewerbe, is the most popular choice for people looking to start personal companies or businesses where the sole trader is responsible for all business debts and actions. If the company’s annual revenue is less than EUR 22000 in first year and less tan EUR 5000 in second year, then the sole proprieter can run the company as a small business (Kleingewerbe). The registration fees for setting up a Gewerbe ranges between 10 and 40 Euros, depending on the region and necessities for your business.
Business Partnership (also known as Personengesellschaft) in Germany are described as sole propietorships with 2 or more actors (people or companies). Most common types of partnerships are GbR (Gesellschaft bürgerlichen Rechts), a civil law partnership, an OHG (offene Handelsgesellschaft), a general commercial partnership, or a KG (Kommanditgesellschaft), a limited partnership. Corporations are most favorable for entities funded companies and startups. The German corporation (GmbH) requires 25,000 euros as capital but ensure protection of personal finances are well-protected. UG (Unternehmergesellschaft) is an ideal option for any company which don’t have the capital to start an LLC as they can start the enterprise with 1 Euro as starting capital.
Register Business in Germany
One must conform the company name with the Commercial Register after checking that the intended name is available going through the local Chamber of Industry and Commerce or Berlin Chamber of Industry and Commerce. Register your business with the relevant trade chamber to get your license, which gives you the right to get involved in the business. In some trades, one has to obtain a special license in areas such as gastronomy, driving schools, taxi companies, skilled craft businesses, insurance brokers, and others. Then, register with the local tax office and provide the Articles of Association certified by a notary within four weeks of commencing business. Open a business bank account next to your private bank account in Germany as many private banks exclude business use in their terms and conditions.
Pay Taxes
A business can be subjected to up to 14 different types of tax and there are nine payment cycles in every fiscal year. Although Germany’s taxation system is based upon over 40 types of taxes established under strict rules, depending on the taxpayer’s benefits from various deductions and exemptions, foreign corporate entities need to pay only on the income that they generate. Foreign companies in Germany are categorized under the foreign tax act, which apply to German resident taxpayers with over 50% stake in a foreign company and foreign entities established in the country. Moreover, foreign companies are levied a 25% withholding tax on dividends however the dividend tax may be reimbursed in case of double taxation agreement. Foreign corporate entities also need to pay municipal trade tax that ranges from 6%-17%, depending on the location of operation.
Challenges in Setting Up Business
One of the main difficulties that people face in establishing a GmbH is in opening a bank account and associating a relevant know-your-customer (KYC) process. Besides, obtaining a building permit and approval of static calculation is a lengthy procedure and obtaining a water connection can take up to 47 days. Getting electricity to business can take up to 28 days. Moreover, registration of a property is quite a bureaucratic task, which requires six procedures. In case of waiver of pre-emption rights, the municipality needs to be obtained. Getting credit in Germany is a streamlines process to both domestic and foreign investors, but banks expect a written presentation of your business plan or investment about legal structure, cost and profitability projections. Furthermore, inadequate availability of skilled labour, especially in nursing and care, construction and IT industries, etc. makes a strong competition between companies to hire the best people. The modern legal system in Germany handles insolvency with relative efficiency, which takes around 1.2 years.
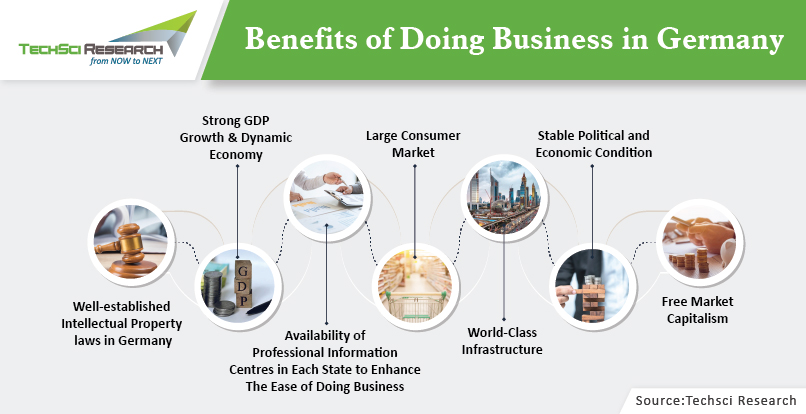
Benefits of Doing Business in Germany
- The well-established intellectual property laws in Germany have been designed to help businesses safeguard their most valuable of assets. The strict competition laws prevent rivals from making false claims about your unique product.
- Since Germany has a dynamic economy and is located in the heart of Europe, it is an ideal springboard for further commercial expansion into neighboring countries like France, Italy, and Austria.
- The Germany government has set up professional information centres in each state to enhance the ease of doing business. Companies seeking to set up in Germany can also visit these centres and enquire about funding, taxes, etc.
- Companies can approach the government to hire a consultant that would help them to come up with a business plan and approach the bank for the loan. The government can pay up to 80% of consultant’s fee as an incentive.



