AI in Cybersecurity: A Game-Changer for Digital Security
In today’s digital world, keeping sensitive information safe from cybercriminals is essential. The cyberattack surface in modern organizations is growing rapidly as hackers are continuously improving their tactics and the organizations are challenged to keep up with the ever-evolving threat landscape. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the cybersecurity landscape. AI and Machine learning are now becoming critical to information security, as these are capable of analyzing millions of data sets and tracking down a wide variety of cyber threats and preventing malware menaces to shady behavior that might result in a phishing attack. AI is not only improving threat detection and response but also helping organizations automate security processes, analyze security events, and identify potential threats before they become a problem.
Threat Detection and Prevention:
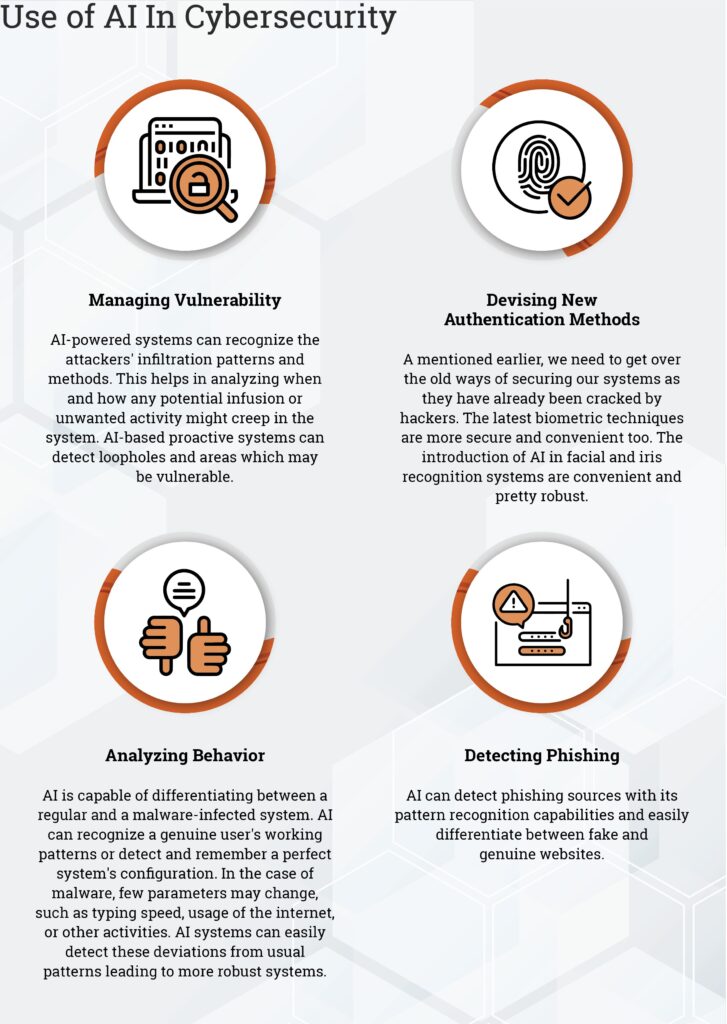
AI is a game-changer in cybersecurity by enhancing security software, detecting, and alerting companies of potential breaches before they occur. AI-powered software can be used to detect internal or external cyber threats and possibly malicious activities, abnormal behaviors, and even predict future threats and attacks. Traditional software systems lack in the sheer number of new malwares created every week, so this is an area where AI is really helpful. This means that companies can take pre-emptive measures before incidents happen rather than trying to mitigate their impact afterward. AI allows for superior predictive intelligence with natural language processing that enables data curation on its own by scraping through articles, news, and studies on cyber threat and with the use of sophisticated algorithms, AI systems can detect malware, run pattern recognition, and detect even the minutest behaviors of malware or ransomware attacks. The systems powered by AI based cybersecurity can furnish the latest knowledge of global as well as industry-specific dangers to better formulate vital prioritization decisions based on what could be used to attack the systems and what is most likely to be used to attack the systems.
According to TechSci Research report “Global Cyber Security Market, By Component (Hardware, Software, Services), By Security Type (Network Security, Content Security, Application Security, Endpoint & IoT Security, Others), By Deployment Mode (Cloud, On-Premises), By End User (BFSI, Healthcare, Aerospace & Defense, IT & Telecommunication, Government, Retail, Manufacturing, Others), By Region, Competition, 2018-2028,” the global cybersecurity market is a rapidly evolving and is a critical sector in today’s digital age. With the pervasive and growing threat of cyberattacks, organizations across the world are increasingly recognizing the importance of investing in robust cybersecurity solutions to protect their sensitive data, critical infrastructure, and digital assets. This expansive and dynamic sector encompasses a wide array of products, services and solutions, which are designed to protect sensitive data, digital assets, privacy in the digital realm. The driving forces underpinning the growth of the global cybersecurity market are multifaceted.
Moreover, the regulatory landscape has undergone a seismic shift, further propelling the growth of the cybersecurity market. Governments across the world have regulated data protection laws, which are designed to safeguard individuals’ personal information and hold organizations accountable for data breaches. Also, the digital transformation of business is another pivotal driver of the cybersecurity market.
However, there are certain challenges that the market faces such as evolving cyberthreat landscape and complexity, skills shortage. High profile incidents of cyberattacks such as ransomware attacks, supply chain compromises, and nation-state sponsored cyber espionage highlight the adaptability and audacity of cybercriminals and threat actors. The market faces the challenge of staying ahead of these evolving threats. More and more organizations are turning to AI and Machine learning to enhance their threat detection capabilities by identifying data patterns and anomalies in real time.
Another significant challenge facing the market is the shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals. There is an increased demand for cybersecurity expertise, which far exceeds the current available pool. This demand is fueled by increasing frequency and complexity of cyber threats and the need for regulatory compliance. The cybersecurity field is highly dynamic and requires professionals to stay updated with evolving technologies, threats and compliance requirements. Finding individuals with the breadth and depth of expertise required for these roles in challenging.
Malware Analysis and Detection:
A large number of Malware has been discovered in the past few decades. These include The Morris Worm, Melissa, Code Red, ILOVEYOU, Sasser, Nimda, Slammer, Welchia, Commwarrior-A, Stuxnet, and CryptoLocker. Malware or malicious applications may cause catastrophic damages to not only computer systems but also data centers, web, and mobile applications to various industries; particularly, financial and healthcare institutes.
Hackers are continuously modifying malware to evade detection, thus making it challenging for traditional signature-based antivirus software to detect new strains of malware successfully. AI-powered malware detection tools leverage artificial intelligence technologies that can analyze and identify malware files based on their behavior. This means that hackers are finding it increasingly harder to bypass the security measures that organizations have put in place. Thus, Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be an effective solution that can be adopted for the development of AntiMalware Systems.
Security analytics and incident response:
The rise of AI has improved security analytics and incident response for detecting and responding to security incidents. AI algorithms are capable of sifting through the vast amounts of security logs that are generated by devices, applications, and systems within an organization and quickly identify incidents, which previously may have gone unnoticed. Security analysts can then respond to incidents faster, limiting the damage to the organization.
Automating security processes:
Another benefit of AI in cybersecurity is its ability to automate security processes, making it more effective and efficient. The use of AI-powered automation can help cybersecurity teams in getting improved insights, enhancing productivity, and improving the economies of scale. With AI, vulnerabilities are detected, and incidents are managed automatically, allowing security teams to focus on the more challenging problems that require human intervention. This not only improves the security posture of an organization, but it also frees up security staff to work on other essential projects.
Facing a talent shortage, organizations are also turning to artificial intelligence to boost productivity of their overstretched resources. AI plus automation can help in better management of the sheer volume and speed of security threats for an organization.
Issue of Bots
Bots are autonomous programs that access and analyze data sources to perform specific tasks. In cybersecurity, bots are used to identify, analyze, and respond to potential security threats in real-time. They can quickly identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a cyber-attack and respond accordingly to prevent or mitigate damage.
With the proliferation of cyber-attacks and the increasing demand for cybersecurity solutions, bots are becoming an essential tool for businesses of all sizes. They are helping to level the playing field, providing even small businesses with the ability to protect against cyber threats. Additionally, bots are constantly evolving, with new and more advanced technologies emerging all the time. As bots become increasingly sophisticated, they will continue to change the game in cybersecurity, making our digital world safer and more secure.
Also, Bots are useful in performing repetitive tasks and imitate human user behaviour. However, Bots make up a huge chunk of internet traffic and can lead to data fraud and account tampering and takeover with stolen credentials.
Downsides of AI in Cybersecurity
Despite its many advantages, the use of AI in cybersecurity comes with its own set of limitations. Some of the disadvantages include:
1. Reliance on AI: One of the main downsides of AI in cybersecurity is over-reliance. Many organizations may be drawn into believing that AI is the ultimate solution to their cybersecurity challenges and may end up relegating human agents. Although AI is effective in detecting cyber threats, it’s not bulletproof. There are still a lot of threats that AI may not be able to detect, and it’s therefore important to keep humans in cybersecurity processes to oversee and complement AI.
2. Expensive: Organizations require more resources and financial investments in order to build and maintain an AI system. Acquiring the data sets is very time-intensive and requires large investments on the part of the organizations, which they cannot afford. The technology requires high-end systems, powerful processors, and large amounts of data to ensure that the AI algorithms have adequate data to train. This adds up to significant costs, which may be out of reach for many small businesses. The cost of implementing AI in cybersecurity should be weighed against its potential benefits and the size of the organization.
3. Diversity of Threats: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and AI algorithms rely on historical data to detect and predict threats. This means that if a new threat emerges, the AI algorithms will not be able to detect it, as there is no historical data to train on. Cybercriminals can also deliberately create new threats that AI algorithms have not seen before to bypass detection and compromise security systems.
- AI-powered malware
The most immediate threat posed by AI in cybersecurity is the development of AI-powered malware. With the ability to learn and adapt on the fly, AI-powered malware can easily evade traditional security measures and cause extensive damage. Attackers can easily target specific individuals or organizations, infiltrate networks, and steal sensitive data. Moreover, once AI-powered malware is deployed, it can continue to learn and evolve, making it even more challenging to detect.
- Adversarial AI
Another concern is the threat of adversarial AI. Adversarial AI can be used to exploit vulnerabilities in AI systems themselves. Attackers can manipulate machine learning algorithms and cause them to behave in unexpected ways, leading to consequences such as false positives or negative outcomes. This poses a significant challenge for security professionals, who must assume that attackers will use adversarial AI to undermine their defenses.
4. Cyberattacks on AI: Cybersecurity systems that rely on AI can also be a target for cybercriminals. If the system is breached, the cybercriminals can manipulate the security algorithms, feeding them with false data to generate false alarms or conceal malicious activities. AI-designed cybersecurity systems can also be vulnerable to “adversarial AI attacks”, where criminals manipulate the AI system into misclassifying data.
5. False Positives and False Negatives: AI algorithms are also not perfect, and they can generate false positives, which occurs when legitimate actions are mistaken and flagged as a security threat. False negatives are also a possibility, and this occurs when potential cyber threats are not detected. Both false positives and false negatives can cause a lot of challenges in cybersecurity and can undermine the effectiveness of AI algorithms.
In summary, the use of AI in cybersecurity has both benefits and downsides. Organizations need to weigh the benefits and costs of implementing AI. They should also keep in mind that AI is not a panacea to all cybersecurity problems and that it works best when used alongside human agents. Cybersecurity is an evolving industry, and it’s essential to adapt to changing trends and threats. A cybersecurity policy that addresses both AI and human agents’ limits ensures maximum protection against cyber threats.
According to TechSci Research report “Artificial Intelligence (AI) Market By Offering (Hardware, Software, Services), By Application (Image Recognition, Natural Language Processing, Speech Recognition, Computer Vision, Other), By Business Function (Finance, Security, Human Resource, Law, Marketing & Sales, Operations, Supply Chain Management), By End User (BFSI, Fashion and Retail, Healthcare and Life Sciences, Manufacturing, Automotive, Aerospace and Defense, Construction, Other), By Region, Competition, 2018-2028,” the global artificial intelligence (AI) market is experiencing a transformative revolution, with its influence permeating virtually every facet of our modern world.
The market growth is driven by various factors, such as rapid technological advancements and innovation in AI, growing adoption across various industries, expanding data ecosystem and supportive government initiatives. The advancements and innovations span across the wide spectrum of AI technologies, including natural language processing, computer vision, machine learning and reinforcement learning. AI algorithms have become more sophisticated with the increased proliferation of data. Moreover, advancements in hardware, such as the development of powerful graphics processing units (GPUs), and dedicated AI accelerators have boosted the efficiency and speed of AI computations. As AI technologies continue to evolve, there are expected to more transformative applications in healthcare, finance and transportation, solidifying AI’s position as a game changing force in the global market.
Also, the growing data ecosystem is key driver of the market as AI algorithms thrive on data, and the increasing digitization has led to explosion of data generation. Also, the augmentation of IoT devices, e-commerce and social media platforms enriches the data pool available for AI analysis. Big data analytics, along with AI enables organizations to unlock previously hidden opportunities, optimize operations and gain a competitive edge. Moreover, data sharing platforms are further increasing the availability of data for AI development.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, AI is a game-changer in cybersecurity. It is not only improving threat detection and response but also helping organizations automate security processes, analyze security events, and identify potential threats before they become a problem. AI-powered software can detect abnormal behaviors, identify internal or external threats, and even predict future threats and attacks. Companies that take advantage of AI in cybersecurity will experience more effective, efficient, and intelligent security checks. With AI, companies can feel more confident that their information is safe from hackers and cybercriminals. Moreover, AI is useful in discovering and prioritizing risks, in direct incident response, and in identifying malware attacks before they come into the picture.
So, despite its potential downsides, AI will serve to drive cybersecurity forward and help organizations create a more robust security posture.



