Product Review: Medtronic PillCam™ Capsule
Medtronic has always remained at the forefront of innovation, evolving products through continuous technological innovations to meet the changing needs of patients and caregivers as well as needs of physicians. PillCam™ capsule is one such breakthrough digital imaging and smart diagnostic tool, offered by the company for accurate diagnosis of the abnormalities present in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. With the expanding demand for wireless capsule endoscopy (WCE), PillCam™ capsule has become increasingly utilized imaging modality, which provides a diagnostic yield close to 60-70%. Medtronic offers different variants for the examination of various parts of gastrointestinal tract, such as oesophagus, small intestine, and colon. The vitamin-pill sized capsule is made up of biocompatible material so that it naturally passes through the anus once it navigates throughout the GI tract. The wireless capsule transmits more than 50,000 images of the small bowel to the receiver worn by the patient, which allows the physicians to review and identify potential abnormalities.
PillCam™ SB1 video capsule endoscope (CE) was the first original non-invasive wireless introduced by the company. The device consisted of a light source, lens, CMOS imager, a battery, and a wireless transmitter. PillCam™ SB1 capsule used to take two images per second and had a battery life of 8 hours. The capsule had an angle of view of 140 degree and magnification ratio of 8:1. To enhance the performance of the imaging device, Medtronic launched PillCam™ SB2, which has the same size as that of SB1 but differ in certain features. PillCam™ SB2 has a broader angle of view of 156 degrees to cover more mucosal surface area at a working distance of 4.5 mm from the dome of capsule and includes a three-lens system. With improved optics of PillCam™ SB2, the entire circumference of intestinal folds can be visualized. The new sophisticated algorithms provided by the photosensitive chip produce images with uniform exposure for a higher image resolution, depth of view, and better sharpness of the mucosal detail.
The third-generation system, PillCam™ SB3 offers a 30% improvement in image resolution and has the capacity to increase number of photographic frames from 2 to 6 per second in relation to the speed at which capsule endoscope navigates in the small bowel. The increased frame per second rate can influence the detection of more lesions in duodenum and jejunum. The image sharpness, natural tissue colours, balanced illumination, and overall image quality in PillCam™ SB 3 is better than PillCam™ SB 2’s. The dynamic nature of Adaptive frame rate technology makes PillCam™ SB 3’s approach to image acquisition efficient and uniquely suited to each patient’s motility. The PillCam™ SB 3 System gives physicians the flexibility to see precisely inside the small bowel which they would not have been able to see otherwise.
Acquiring Covidien Inc., US-based Medtronic started the ball rolling on non-invasive imaging to provide images inside of the GI tract. The platform has been further developed with introduction of more variants of PillCam™ technology in the following years to enhance patient’s experience and usability of their clinical device. Following the footsteps of Medtronic, other companies also launched capsule endoscopy devices, owing to the rising demand for non-invasive optical endoscopy and incessantly increasing and persistent digestive disorders. Currently, EndoCapsule from Olympus is giving a fierce competition to the PillCam™ capsules that utilizes different optimization techniques for digital imaging. Intromedic’s MiroCam®, Jlinshan’s OMOM, among others are most sought after non-invasive wireless endoscopy devices.
According to TechSci research report on “Global Endoscopy Capsule Market By Product Type (Small Bowel, Esophageal, Colon) By Accessories (Wireless Capsule v/s Workstation and Receiver) By Endoscope Type (Capsule Cystoscopies v/s Capsule Neuro-Endoscopes) By Application (OGIB (Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding), Crohn’s Disease, Small Intestine Tumor, Others) By End User (Hospitals & Clinics, Ambulatory Care Center, Others) By Company, By Region, Competition Forecast & Opportunities, 2026”, the global endoscopy capsule market is forecast to witness impressive growth in the next five years on account of increased demand of non-invasive methods for diagnosis purposes.
Detailed Competition Analysis of PillCam™ Capsule Endoscope
Image Quality
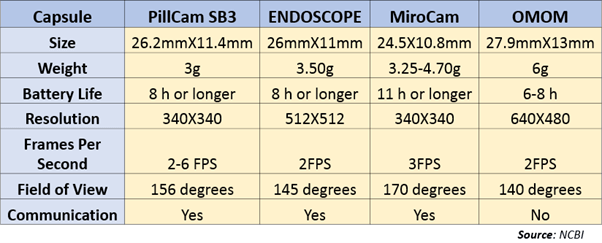
Image quality is one of the most significant factors in capsule endoscopy that largely influences the ability of physicians to make proper clinical diagnosis. The first generation PillCam™ SB had an image sensor resolution of 256X256 pixels, which remained standard for all PillCam™ capsules, but the latest generation SB, the SB3 has an image resolution of 340X340 pixels. Other capsule endoscope available in the market such as EndoCapsule from Olympus offers a resolution of 512X512 pixels, or MicroCam from IntroMedic has a resolution of 320X320 pixels, which results in high image resolution images with less noise and halation that ultimately better diagnosis of the GI tract diseases.
Diagnosis
For the accurate and reliable diagnosis of each part of the gastrointestinal tract, Medtronic offers several variants incorporating same technology but differs in terms of design, features, image resolution, lens angle, frame rate, LEDs, and battery life.
PillCam™ Crohn’s (PCC) combines a long-lasting battery life of up to 14 hours with two adjustable frame-rate wide-angle cameras and software. PCC facilitates efficient reading of capsule endoscopy for both small bowel and colon. One important limitation of the PillCam™ Crohn’s capsule is the requirement for vigorous colonic preparation. Although the small bowel capsule is user-friendly, extensive preparation may hamper patient’s willingness to undergo the procedure.
The PillCam™ COLON 2 capsule endoscopy system allows nearly 360° coverage of the colon. The 1.6 mm × 31.5 mm in size colon capsule is equipped with an adaptive frame rate to enhance colon visualization and save battery. The colon capsule captures 35 images per second when in motion and 4 images per second in stationary state. Then, the data recorder controls the capsule image rate in real time while analysing the capsule images. The software includes a tool for the estimation of polyp size and distance in colon. The high sensitivity for clinically relevant lesions coupled with the safety profile and potential high acceptability make PillCam™ COLON capsule endoscopy a valuable option for diagnostic colonic techniques.
The PillCam™ UGI System consists of two optical heads enclosed inside the capsule, which travels through the patient’s upper GI tract and captures detailed and precise images at a rate of 18 to 35 frames per second. The PillCam™ UGI system has a minimum operating time of 90 minutes and is resistant to dissolution in pH=2-pH=8. Physicians use the capsule for visualization of the upper gastrointestinal tract (oesophagus, stomach, duodenum) in patient above 18 years of age. Some of the risks associated with usage of PillCam™ UGI capsule include capsule retention, aspiration, and skin irritation.
PillCam™ ESO 3 capsule intends visualization of oesophageal mucosa, capturing images at the rate of 35 frames per second. The video capsule is equipped with two miniature colour cameras, battery, and an LED light source. The brief travel time and immediate entry into the oesophagus allow for the PillCam™ ESO to have a short battery that works for 30 minutes.
Cost
Medtronic’s PillCam is one of the most popular as well costlier alternatives for wireless endoscopy. The Chinese counterpart offers the capsule endoscopy at relatively low price than PillCam™ CE system, which makes it relatively cost-effective option.
With lightweight and compact design coupled with 10-hour battery life, the Jinshan’s OMOM CE has become increasingly popular. Inbuilt suspected GI bleeding detection functionality selects images of relevance for the physician. Since the position of the capsule, including movement and angle of OMOM CE can be controlled, it allows more comprehensive imaging of the stomach.
Device Manoeuvrability
The capsule endoscope has seen significant advancements over the past 20 years, yet it still shows great potential for improvement in device manoeuvrability. Enabling the guidance of capsule could allow targeted investigation which could open possibilities of direct drug delivery to the areas of interest. Controlling the capsule from externally could help to reduce the overall power consumption of the device, which could be used for image collection and transmission. However, IntroMedic’s MiroCam® Navi consists of an external magnetic controller to manoeuvre the device.
Video Reading Time
The Omni Mode technology in Olympus’s ENDOSCOPE cut reading time significantly (by 64%) while seeing everything of importance for the diagnosis. Supporting a safe detection process, Omni Mode also ensures that everything captured by the capsule is shown, without the usual duplication of the images. PillCam CE system does not offer that kind of flexibility to the physicians. The PillCam RapidView software allows the proportion of images excluded to be determined by the reader. When compared with alternative time-saving strategies, the PillCam software proved to be less promising in saving time.
Conclusion
As first to the market, PillCam is the most widely used wireless capsule endoscopy, boasting high image resolution, adaptive frame rate technology, and 3D tracking function. MiroCam capsule offers magnetically steerable capsule for the examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract, enabling a long battery life despite its smaller dimensions. The OMOM capsule boasts duplex data communication, which allows real-time adjustments of parameters such as frame rate, brightness, exposure to optimize the quality of examination.
With the advancement in technology, the capabilities of the capsule endoscope have progressed. From the introduction of PillCam™ SB to the release of the current PillCam™ COLON 2, the capsule endoscope has undergone major changes in terms of resolution, view angle, frame rate, and power consumption. However, future capabilities such as targeted drug delivery and automated locomotion could even broaden the application of this device.