Hand Gesture Recognition: A Powerful Tool for Natural Interaction
In a world where human-computer interaction is becoming increasingly seamless and intuitive, hand gesture recognition (HGR) emerges as a remarkable technology, bridging the gap between users and machines through natural movements. From controlling virtual environments to aiding communication for the hearing impaired, HGR holds immense potential across various domains. In the automotive sector, this capability enables both drivers and passengers to engage with the vehicle, primarily for managing the infotainment system, all without the need for physical contact with buttons or screens. In this blog, we’ll delve into what HGR is, how it works, its applications, and the benefits and challenges associated with its implementation.
What is Hand Gesture Recognition?
Hand Gesture Recognition (HGR) refers to the technology which enables computers to interpret and understand human hand movements. It allows users to interact with devices and applications through gestures, mimicking the way we naturally communicate with each other. By capturing and analyzing the motion of hands, HGR systems translate these movements into commands or actions, offering a more intuitive and immersive user experience. A hand gesture recognition system offers a natural, innovative, and contemporary method of non-verbal communication. Its applications span across various domains, including human-computer interaction and sign language interpretation.
How Does Hand Gesture Recognition Work?
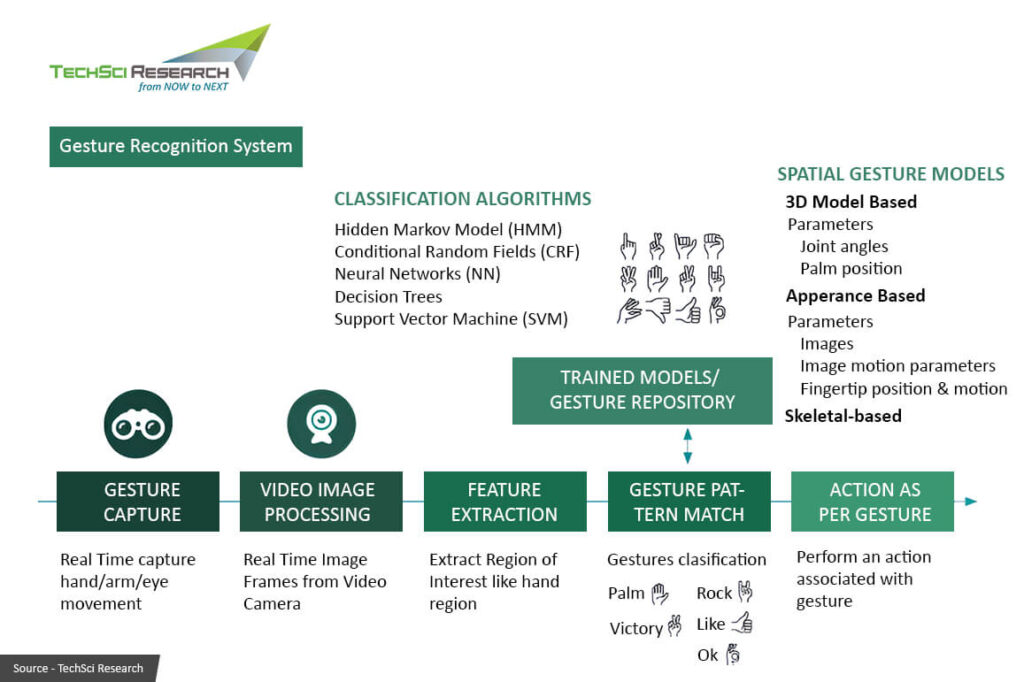
The process of hand gesture recognition involves several key steps:
Data Acquisition: Hand Gesture Recognition (HGR) systems utilize cameras or specialized sensors to capture either video or depth data depicting hand movements. These sensors meticulously record the motion dynamics of the hand, laying the foundation for subsequent analysis.
Preprocessing: This pivotal step involves the refinement and enhancement of the acquired data. Through sophisticated algorithms, noise is meticulously filtered out, and the data is polished to ensure optimal accuracy. Preprocessing plays a crucial role in preparing the data for the subsequent stages of analysis.
Hand Detection and Tracking: Once the data is refined, the system embarks on isolating the hand region within the captured frame. Employing advanced computer vision techniques, the system meticulously identifies and delineates the contours of the hand, enabling precise tracking of its movement over time. This dynamic tracking capability is essential for interpreting gestures accurately in real-time scenarios.
Feature Extraction: With the hand movements tracked, the system proceeds to extract pertinent features from the captured data. Key points such as fingertips, the center of the palm, and hand orientation are meticulously identified and extracted. These features serve as crucial descriptors that encapsulate the essence of each gesture, facilitating subsequent classification.
Gesture Classification: In the final stage, machine learning algorithms come into play to discern and categorize specific gestures based on the extracted features. Leveraging sophisticated classification techniques, these algorithms meticulously analyze the input patterns and assign them to corresponding actions. Through extensive training on a meticulously curated dataset of labeled gestures, these algorithms adeptly learn to recognize and interpret a diverse array of hand gestures with remarkable accuracy.
By seamlessly navigating through these intricate stages, hand gesture recognition systems empower users with a natural and intuitive means of interaction, transcending conventional input modalities and paving the way for enriched human-computer interaction experiences.
Applications of Hand Gesture Recognition
Hand Gesture Recognition finds a myriad of applications across different industries, including:
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Control: Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Control represent groundbreaking applications of gesture recognition technology, revolutionizing the way users engage with digital environments and interfaces. Through intuitive hand gestures, users can seamlessly navigate virtual worlds, interact with virtual objects, and manipulate interfaces, fostering unparalleled immersion and usability.
In Virtual Reality (VR) environments, gesture recognition enables users to explore and interact with virtual spaces in a manner akin to real-world interactions. By simply gesturing with their hands, users can manipulate virtual objects, traverse virtual landscapes, and engage with complex interfaces with remarkable fluidity and precision. This intuitive mode of interaction enhances the immersive qualities of VR experiences, allowing users to suspend disbelief and become fully immersed in virtual environments.
Similarly, in Augmented Reality (AR) applications, gesture recognition empowers users to interact with digital content overlaid onto the physical world. Whether it’s navigating augmented interfaces, manipulating virtual objects within real-world environments, or engaging with AR-based gaming experiences, gesture control adds a layer of naturalness and intuitiveness to AR interactions. By leveraging hand gestures, users can seamlessly integrate digital content into their physical surroundings, blurring the lines between the virtual and real worlds.
The integration of gesture recognition technology in VR and AR systems not only enhances user experience but also unlocks new possibilities for creative expression, collaboration, and productivity. By removing the barriers imposed by traditional input devices such as controllers or keyboards, gesture-based interactions enable users to interact with digital content in a more intuitive and expressive manner. This not only enhances the accessibility of VR and AR experiences but also opens up new avenues for innovation and experimentation in fields such as gaming, design, education, and training.
Furthermore, gesture-based interactions in VR and AR have practical implications across various industries. From architectural visualization and industrial design to medical training and virtual prototyping, gesture recognition technology facilitates hands-on interactions with complex digital models and simulations, empowering users to manipulate, analyze, and interact with data in a more natural and intuitive manner.
Sign Language Recognition and Communication Assistance:
HGR enables real-time interpretation of sign language gestures, facilitating communication for the hearing impaired. By harnessing the capabilities of gesture recognition technology, HGR systems can offer real-time interpretation of sign language gestures, bridging the communication gap between individuals who use sign language and those who do not. For the hearing-impaired community, sign language serves as a primary mode of communication, allowing them to express thoughts, convey emotions, and engage in meaningful interactions. However, for individuals who do not understand sign language, communication barriers can often arise, leading to feelings of isolation and exclusion. This is where HGR technology emerges as a transformative solution, enabling real-time translation of sign language gestures into spoken language or text, thereby facilitating seamless communication between individuals with differing communication abilities.
Through sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models, HGR systems analyze and interpret the intricate hand movements and gestures inherent in sign language. By recognizing and deciphering the unique gestures, hand shapes, and movements associated with specific signs, these systems can accurately translate sign language into spoken words or written text in real time. This enables individuals who do not understand sign language to effectively communicate with and comprehend the messages conveyed by those who use sign language as their primary means of communication.
Moreover, HGR technology can also empower individuals with hearing impairments to engage more effectively with digital devices and platforms. By integrating gesture recognition capabilities into assistive technologies and communication devices, individuals with hearing impairments can use hand gestures to navigate interfaces, access information, and communicate with others more independently and effectively.
Furthermore, HGR-based communication assistance solutions can be customized to cater to the specific needs and preferences of users, offering personalized support for different sign language dialects, communication styles, and levels of proficiency. This adaptability and flexibility make HGR technology a valuable tool for fostering inclusive communication environments and empowering individuals with hearing impairments to participate more fully in social, educational, and professional settings.
Human-Robot Interaction:
Gesture-based Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) not only offers an intuitive and natural communication method but also provides an avenue to enhance the interaction between humans and robots. By leveraging gestures, users can seamlessly convey commands or intentions to robots, fostering smoother and more efficient exchanges. This innovative approach holds promise for revolutionizing the way humans and robots collaborate, leading to enhanced productivity and user satisfaction in various domains.
Automotive (infotainment systems):
Drivers can control in-car entertainment systems, navigation, and other functions through hand gestures, reducing distractions and enhancing safety. A gesture recognition system initiates with a strategically positioned camera focused on a designated three-dimensional area within the vehicle, meticulously capturing frame-by-frame images depicting hand positions and movements. Typically housed in the roof module or another unobtrusive vantage point, this camera ensures uninterrupted visibility. To optimize image clarity, especially in low-light conditions, the system employs infrared LEDs or lasers to illuminate the area.
These captured images undergo real-time analysis facilitated by cutting-edge computer vision and machine learning technologies. These advanced algorithms discern intricate hand gestures and translate them into actionable commands, drawing from a pre-established library of gestures.
The commands derived from the gesture recognition software seamlessly integrate into the vehicle’s interface, akin to conventional input methods such as adjusting dials, pressing buttons, or interacting with touch screens. Moreover, with advancements in cabin camera technology, there is potential for other passengers within the vehicle to participate in gesture-based interactions, further enhancing the overall user experience.
Gaming and entertainment:
In the realm of gaming and entertainment, hand gesture recognition (HGR) serves as a game-changer, quite literally. It introduces an exciting dimension to gaming experiences by empowering players to control characters and navigate virtual environments using nothing but their natural hand movements. This technology transcends traditional input methods, such as keyboards, controllers, or touchscreens, offering a more immersive and intuitive way to engage with games.
Moreover, HGR opens up new possibilities for multiplayer experiences, fostering collaboration and competition in ways previously unexplored. Players can communicate non-verbally through gestures, coordinate strategies with teammates, or engage in lively virtual interactions, enriching the social aspect of gaming.
Medical rehabilitation:
In the domain of medical rehabilitation, the integration of hand gesture recognition (HGR) offers tremendous potential for enhancing the recovery process for patients undergoing rehabilitation for hand injuries, surgeries, or neurological conditions. By incorporating HGR into therapy sessions, healthcare professionals can create personalized and interactive exercises tailored to each patient’s specific needs and capabilities.
Potential Future Applications
As technology continues to advance, the potential applications of Hand Gesture Recognition are boundless. Future developments may include its integration into smart home systems, retail interfaces, education platforms, and more, further revolutionizing the way we interact with technology and each other.
Benefits and Challenges of Hand Gesture Recognition
Benefits:
Intuitive interaction: HGR offers a natural and instinctive way to interact with devices and applications, reducing the learning curve for users.
Contactless control: By eliminating the need for physical touch or input devices, HGR promotes hygienic and touch-free interactions, particularly relevant in a post-pandemic world.
Accessibility: HGR opens up new possibilities for individuals with physical disabilities or limitations, providing alternative means of communication and control.
Challenges:
Accuracy in varying conditions: HGR systems may struggle to maintain accuracy under changing lighting conditions, occlusion, or background clutter, requiring robust algorithms and preprocessing techniques.
Computational cost: Real-time gesture recognition demands significant computational resources, posing challenges for implementation on resource-constrained devices.
Complexity of real-time recognition: Achieving low-latency, real-time performance while maintaining accuracy and reliability remains a key challenge in HGR research and development.
According to TechSci Research report “Gesture Recognition Touchless Sensing Market – Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, Segmented By Technology (2D, 3D, Sensors), By Product (Touch-Based Gesture Recognition, Touch-Less Gesture Recognition), By Application (Entertainment, Consumer Electronics, Healthcare, Hospitality, Retail, Others), By Region, and By Competition, 2019-2029F,” the Global Gesture Recognition Touchless Sensing Market was valued at USD 19.07 billion in 2023 and is predicted to experience robust growth in the forecast period with a CAGR of 22.73%. The market growth is driven by various factors, such as rising demand for hygienic interaction solutions, increasing integration in consumer electronics, advancements in sensor technology, growing interest in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), expansion of automotive gesture control systems, and adoption in healthcare and medical applications.
Factors Driving the Growth of Gesture Recognition Touchless Sensing Market
- Rising Demand for Hygienic Interaction Solutions
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of hygiene and cleanliness in public spaces and shared environments. As a result, there has been a surge in demand for touchless interaction solutions that minimize physical contact with surfaces. Gesture recognition touchless sensing technologies offer a hygienic alternative to traditional touch-based interfaces, driving their adoption in sectors such as retail, hospitality, healthcare, and transportation.
- Increasing Integration in Consumer Electronics
Gesture recognition touchless sensing technology is increasingly being integrated into consumer electronics devices such as smartphones, tablets, and smart TVs. Manufacturers are leveraging this technology to enhance user experiences, improve accessibility, and differentiate their products in the competitive market landscape. The convenience and intuitiveness of gesture-based interactions appeal to consumers seeking seamless and engaging user interfaces.
- Advancements in Sensor Technology
Continual advancements in sensor technology, particularly in areas such as depth sensing, infrared imaging, and machine vision, have significantly improved the accuracy, reliability, and versatility of gesture recognition touchless sensing systems. These technological innovations have expanded the scope of applications for gesture recognition across diverse industries, driving market growth and adoption.
- Growing Interest in Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
The growing interest in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) experiences is driving the demand for gesture recognition touchless sensing technology. Gesture-based interactions enhance immersion and interactivity in AR/VR environments, enabling users to manipulate virtual objects, navigate interfaces, and engage with content in more intuitive ways. As AR and VR applications continue to proliferate across gaming, education, training, and enterprise sectors, the demand for gesture recognition touchless sensing solutions is expected to soar.
- Expansion of Automotive Gesture Control Systems
Automotive manufacturers are increasingly integrating gesture recognition touchless sensing systems into vehicles to enable gesture-based control of infotainment, navigation, and driver assistance features. Gesture control offers drivers and passengers a hands-free and intuitive way to interact with in-car systems, enhancing convenience, safety, and user experience. With the rise of autonomous and connected vehicles, the demand for advanced gesture control solutions in the automotive sector is poised for significant growth.
- Adoption in Healthcare and Medical Applications
In the healthcare sector, gesture recognition touchless sensing technology is being leveraged for a variety of applications, including hands-free operation of medical devices, touchless patient monitoring, and interactive rehabilitation systems. These applications enhance patient comfort, reduce the risk of cross-contamination, and improve overall efficiency in healthcare delivery. As healthcare providers increasingly prioritize patient safety and infection control, the demand for gesture recognition touchless sensing solutions is expected to rise.
Thus, the global gesture recognition touchless sensing market is experiencing rapid growth driven by factors such as the rising demand for hygienic interaction solutions, increasing integration in consumer electronics, advancements in sensor technology, growing interest in AR/VR, expansion of automotive gesture control systems, and adoption in healthcare and medical applications. As businesses and consumers continue to embrace touchless interaction solutions, the gesture recognition touchless sensing market is poised for sustained expansion and innovation in the years to come.
According to TechSci Research Report “Gesture Recognition Market – Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, Segmented By Technology (Touch-based, Touchless), By Industry (Automotive, Consumer Electronics, Healthcare, Others), By Region, By Competition 2019-2029F,” Global Gesture Recognition Market was valued at USD 15.7 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to project robust growth in the forecast period with a CAGR of 31.4% through 2029. The market growth is driven by various factors, such as rising demand for intuitive interfaces, proliferation of smart devices, advancements in sensor technology, etc.
Factors Driving the Growth of Global Gesture Recognition Market:
- Rising Demand for Intuitive Interfaces: As technology becomes increasingly integrated into our daily lives, the demand for intuitive interfaces has surged. Gesture recognition, with its ability to interpret natural human movements, offers a user-friendly alternative to traditional input methods such as keyboards and touchscreens. This heightened demand for seamless interaction experiences across various devices and applications serves as a significant catalyst for market growth.
- Proliferation of Smart Devices: The proliferation of smart devices, ranging from smartphones and tablets to wearables and smart home appliances, has created a fertile ground for gesture recognition technology to flourish. Consumers seek devices that not only offer advanced functionalities but also simplify their interaction with technology. Gesture recognition, by enabling hands-free and touchless control, enhances the user experience and aligns with the evolving preferences of tech-savvy consumers.
- Advancements in Sensor Technology: The rapid advancements in sensor technology have been instrumental in driving the evolution of gesture recognition systems. From depth-sensing cameras and infrared sensors to radar and LiDAR technologies, the market has witnessed a surge in innovative sensor solutions capable of accurately capturing and interpreting gestures in real-time. These technological advancements have expanded the scope and capabilities of gesture recognition applications, fuelling market growth.
- Growing Adoption in Healthcare and Automotive Sectors: Gesture recognition technology has found compelling applications in sectors such as healthcare and automotive, where hands-free interaction is paramount. In healthcare, gesture-controlled interfaces facilitate touchless operation of medical devices and improve hygiene standards in clinical settings. Similarly, in the automotive sector, gesture recognition systems enhance driver safety and convenience by enabling gesture-based control of infotainment systems and driver-assistance features.
- Emergence of AI and Machine Learning: The convergence of gesture recognition technology with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning has unlocked new possibilities in terms of gesture interpretation and recognition accuracy. Machine learning algorithms, trained on vast datasets of human gestures, continuously improve the accuracy and reliability of gesture recognition systems, thereby driving their adoption across diverse applications and industries.
- Demand for Contactless Solutions Amidst COVID-19 Pandemic: The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of contactless interaction solutions to minimize the risk of virus transmission. Gesture recognition technology, offering touchless control and interaction, has witnessed increased adoption in public spaces, retail environments, and healthcare facilities as a means to mitigate the spread of the virus. This heightened demand for contactless solutions has contributed to the growth of the gesture recognition market.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, hand gesture recognition emerges as a transformative technology with vast applications and immense potential to revolutionize human-computer interaction. Despite the inherent challenges it presents, the advantages it brings in terms of intuitive engagement, enhanced accessibility, and touchless manipulation underscore its importance as a pivotal area of exploration and advancement, paving the way for the evolution of human-machine interfaces in the foreseeable future. As researchers and developers continue to innovate in this field, the possibilities for leveraging hand gestures to augment our digital experiences and streamline our interactions with technology are boundless, heralding a new era of seamless and natural communication between humans and machines.