Future of Drone Technology
Over the past few years, the role of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and drones has been expanding across all sectors of society. As technology continues to permeate into our daily lives, new applications for drones are emerging. Although drones are still in the infancy stage in terms of mass adoption, they continue to break through traditional barriers in industries which seemed impenetrable by similar technological innovations.
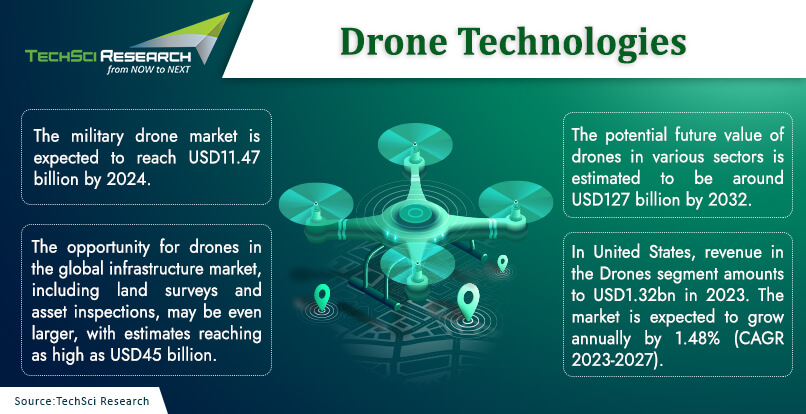
From making quick deliveries at rush hours to scanning unreachable military base, gathering information, or supplying essentials for disaster management to geographical mapping of inaccessible terrain, drones can perform many complex tasks at ease. Besides, drones are being widely used for building inspection, oil and gas refinery inspection, agriculture surveillance and mapping, rescue operations, aerial photography, thermal imaging, and more. However, the potential of drones is far beyond these functionalities. According to statistics, nearly 900,000 drones have been registered in the United States, 63% of which were for recreational purposes and rest for commercial operations. By 2024, the number of recreational drones is projected to peak at around 1.5 million drones and the number of commercial drones is anticipated to double.
Growing Role of Drone Technology in Oil & Gas Sector
Drones are being widely deployed across the oil and gas sector for various applications, in terms of engineering and pure science. Big oil companies such as Shell, ExxonMobil, Royal Dutch, TotalEnergies, etc. have pioneered the drone deployment to obtain real-time insights and enhance their productivity. Earlier the use of drones in oil and gas companies was limited to remote monitoring and surveillance of assets during regular operations, but recent advancements in sensing and imaging technologies have expanded their uses. Wellbore drilling optimization, automated drilling tools, and pressure sensing flow actuators are some of the accelerating innovation areas where the application of drones has been growing. Many commercial drone manufacturers are working in close collaboration with oil and gas companies to make customized applications available for industrial use. In the past three years, over 500,000 patents for AI-assisted drone control have been filed and granted in the oil & gas industry, owing to the growing importance of technologies such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, big data, and IoT.
Drones Empowering Renewable Energy Industry
As the focus of governments across the world is increasing towards energy transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources, the adoption of digitally controlled drones have been gaining rapid popularity. Solar and wind farms are presenting myriad of opportunities for the use of drones to improve efficiency at the plant, reduce overall costs, and reduce time required to carry out various operations. Drones are being widely utilized for inspection of solar and wind farms, cleaning of turbine blades, de-icing of turbine blades, detect failed photovoltaic cells, optimize fitting of solar panels, etc. Using topological information captured through UAVs, developers are stimulating different layouts, which maximize energy generation and minimize externalities. Regular drone inspection can lead to reliable technology onsite and reduce the chances of injuries.
Latest developments in the drone technology–
Drones with AI-based Sensors
Drones enabled with artificial intelligence are rapidly becoming a part of the smart mobility offerings that are now commercially available to businesses and consumers. AI-based drones rely on computer vision, which works through high-performance, onboard image processing enabled with neural network. Neural networks allow drones to perform object detection, classification, and tracking in real-time. The information combined with real-time monitoring helps to avoid collisions, locate, and track targets. Sensors collect information processed by drone systems, including visual, positioning, and environmental data. This data is entered into machine learning models to determine how a drone reacts to a particular environmental condition or objects it should prioritize or avoid.
Drones with Improved Computer Vision
For drones to recognize and react to their surroundings, enterprises are making strides with artificial intelligence. Drones with deep neural networks can help organizations to identify people or objects fed into them to predict which class the image belongs and analyse those images in real-time. Computer vision and remote sensing technologies also enable drones to identify objects while in surveillance with structure datasets, which can allow companies to identify potential threats or items. The 3D sensors can help develop real-time face detection applications that identify an individual in diverse poses, lighting, or expressions with holistic and feature-based approach. Drones powered by edge detection can enable drones to find boundaries withing image using image processing techniques, mainly for pattern recognition, image morphology, and feature extraction.
Drones with Digital-twin Technology
Digitally connecting the physical twin with its digital twin can allow the real drone to be controlled in real life, via the digital twin platform. Integrating physical with digital platform, the lifetime of physical counterpart can be increased. The digital twin technology can create future or real-time simulations that register all the information about surroundings, including the terrain, moving missiles, and even weather. Feeding information in the digital twin dashboard can allow the person in charge of the drone to have better visuals. For the development of smart cities, companies are integrating drones with digital twin technologies to produce 3D interactive models of the infrastructure in short period. Drone remote sensing technology of the city’s real scene can be used for the investigation of the status quo with intuitive feature images, precise geographic locations, and excellent three-dimensional spatial analysis capabilities.
Solar-Powered Drones
Low battery power has always remained a concern for the longevity of drone operations. However, researchers are combining solar power with drone technology to explore the potential uses of solar-powered drones. The advent of thin, flexible, transparent, and lightweight solar panels have made it feasible to power drones. Attaching more efficient solar panels would mean that the drone could stay in the air for longer period. Solar-powered drones can also carry lithium-ion batteries that can allow them to fly at night. Due to lighter weight of solar panels, more batteries can be included, which would add to the endurance of drones. Harnessing solar energy to power UAVs could make operations more efficient and cost-effective and eliminate the need to bring drones back down after a few hours for a charge.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Propulsion Technology for UAVs and Drones
The endurance of UAV is highly influenced by the propulsion technology used and amount of fuel carried. Hydrogen fuel cells offer high energy density than battery technology, which extends the duration of the flight by three-fold. The hydrogen fuel cells work silently and emit no greenhouse gases. The hydrogen tanks can be replaced and refueled in minutes.
Way Ahead
Designers, manufacturers, and other technology professionals are equipping drones with advanced features to enhance flight time and load-carrying capacity, which could further expand the application of drones in the future. The drones that are commercially available use lithium batteries as they are light-weight, and their payload capacity is small. Although these drones work perfectly on batteries for short distances, transporting heavy loads and covering longer distances still presents a challenge. Hence, engineers are exploring new ways to power drones and revolutionize cargo delivery.
A drone prototype, the Rhaegal drone, equipped with a hybrid engine has an incredible lift capacity of 829 pounds. Emergence of such drones can help to expand the role of drones in construction and maintenance of complex and remote facilities. As investment for manufacturing of heavy drones is expected to grow, more such developments in the drone technology can be expected in the future.
According to TechSci Research report on “Drone Market – Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Competition, Opportunity, and Forecast, 2017-2027 Segmented By Type (Fixed Wing Drone, Rotary Blade Drone, Hybrid Drone), By Altitude (MALE, HALE, LALE), By Payload (Less than 200 kg, 200-500 kg, 500-1000 kg, Above 1000 kg), By End User (Commercial, Defense, Recreational), By Application (Logistics, Security, Agriculture, Mining & Construction, Media & Entertainment, Others), By Region”, the global drone market is projected to grow at a significant rate during the forecast period.
The market growth can be attributed to the constantly evolving defence drone technologies, expanding usage of unmanned aerial vehicles for agriculture, mining, and construction activities. Besides, growing demand for drones in delivering packages and developments in battery technologies are some of the factors fuelling the growth of global drone market.



