How is Digitalization Transforming the Face of Mining Industry?
The mining sector has moved beyond the use of explosives and mechanized equipment introduced during the Industrial Revolution. Over time, mining techniques and technologies have evolved and improved, contributing to better practices and strong industrial growth. Currently, the mining industry is under pressure due to declining demand, price volatility, increased costs, undervalued product estimates, growing environmental threats, and rapidly aging mining facilities resulting in the extraction of low-grade ores. The global mining operations are 28% less productive than ten years ago. Hence, the mining industry is undergoing a major strategic transformation to improve productivity, enhance efficiency in operations, and increase profits.
Disrupting the initially established conservatism, digital tools and technologies, digital methods, systems, digitized data, and advanced analytics are being employed to varying degrees across all activities in the mining industry. Digitalization in the mining industry is unlocking new ways of managing variability and advancing the future of work. Adding equipment sensors and a unified network to transmit data, many mining companies have mechanized their operations to transition from physical to digital. Besides integrating data from on-field physical assets, the industry players can improve their ability to analyze real-time information and enhance remote support of work activities. Thanks to digitalization, many organizations are able to focus on driving system-level thinking and performance.
Modern technologies and digital tools changing the face of mining operations are as follows.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles as Mine Scouts
Mining processes are highly labor-intensive and require continuous monitoring of assets. Manual inspections and surveying lead to many critical safety concerns that can result in injury or death within the mining industry while restricting the extent of endeavor. A mining block might stretch to hundreds of acres, for which the supervisors can take weeks or months to evaluate and take necessary action areas across the site. Besides, dangerous fumes and chemicals produced by waste generated from mining operations could create an inhospitable environment for supervisors during long inspection periods, making them susceptible to respiratory health conditions. Thus, drones seem like a viable solution for better and safer operations, reducing the health risks for those involved in scouting and management.
The unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with high-resolution visual and thermal cameras with multi-zoom capabilities have become an indispensable part of the modern mining industry. The supervisor is responsible for setting a flight plan covering the points of interest across the mining site and controlling the camera for a complete 360-degree view of each zone. Thus, drones reduce the time for scouting operations and increase the effectiveness and quality of inspections. The aerial vehicles can easily access hard-to-reach areas, maneuver through rough terrains and collect precious live surveillance data for immediately actionable insights. The use of drones enhances sustainability in the mining sector, reducing unregulated mining operations, often resulting in water contamination, air pollution, deforestation, and loss of human life.
Wireless Sensor Technologies for Efficient Operations
From changing environmental conditions to the explosion, mining operations involve a lot of potential hazards due to the cumbersome nature of machinery used. Hence, mining organizations have started leveraging wireless sensors to monitor various processes, keep personnel safe, and predict maintenance when required. One of the most common sensors used in mining sites is the gas sensor, which predicts the different fumes arising from the veins within the rocks during excavation. These odorless and colorless gases may contain hydrogen cyanide, hydrogen chloride, carbon monoxide, and other hazardous chemicals, which can put miners’ health at risk. Gas sensors measure the amount of gas released from the rocks and their effect on both personnel and machinery present at the mine site, which can help prevent accidents and loss of life. Mine workers need to do a lot of heavy lifting during mining, which reduces their concentration and makes them tired. Hence, they are now being fitted with tracking devices embedded with sensors to measure the level of tiredness so that they do not fall asleep or lose concentration.
Proximity sensors are being fitted on heavy machinery and vehicles used within the mine to alert the driver through visual or audible warnings and prevent any damage if they collide with other machinery or surroundings. Some sensors are also placed in pits, and underground mines where huge rock pieces and unstable rock faces/ceilings are present to prevent rock falls after operational measures. The sensors can be used to spot anomalous trends in data, which can potentially detect downtime in operations.
According to TechSci Research report on “Global Blasting Automation Services Market By Type (Batch Machine, Continuous Machine), By Application (Metal Mining, Non-Metal Mining, Coal Mining), By Company, By Region, Forecast & Opportunities, 2027”, the global blasting automation services market is anticipated to grow at a significant rate during the forecast period. The growth can be attributed to the rising concerns over safety and increased productivity in mining operations.
Virtual Reality (VR) for Training Purposes
The adoption of Virtual Reality technologies is picking up pace in recent years, and they are rapidly becoming an integral part of many industries, and the mining sector is one of them. Since mining operations involve many dangers, inadequate training can cost the lives of personnel. Hence, the mining industry is preparing its personnel to leverage virtual reality technology to prepare them for the actual mining environment to improve their safety, enhance productivity, and reduce costs. Putting the VR headsets on eyes, recruits can experience a virtual environment of the mining site, which provides them a better understanding of what and how to handle different situations. Some of the world’s largest mining companies, including Debswana Mines, Sesa Goa, Rio Tino, among others, are providing customized VR training solutions to provide an immersive learning experience to new recruits and experienced professionals.
Autonomous Haulage Systems for Enhanced Mobility
Ever since the launch of industry 4.0, smart and intelligent machinery has become prominent in every industry. Advancements of robotics in the Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) have led to state-of-the-art automated giant vehicles like Autonomous Haulage Systems (AHS), designed to transport ore from mining sites without human intervention. The smart trucks have the capacity to carry up to 400 tons of ore accurately, which increases the efficiency of operations. Besides, advanced haulage systems operate on a 24/7 schedule with no idling time and improve fuel usage by 4%. The sensing technology assists in collecting data and analysis that helps minimize downtime and optimize operations. A leading player in driverless technology, UK mining company Rio Tino has collaborated with Japan mining equipment manufacturer, Komatsu Limited, to develop technology for driverless trucks. Loaders, excavators, drills, bulldozers, and other vehicles will be automated in the coming years.
Smart Rock Bolts
The active rock reinforcement procedure involves strengthening rock using bolts and anchors but sometimes can damage the rock bolts, leading to tunnel collapses, injuries, or even loss of lives. However, smart rock bolts can minimize the risk of these kinds of catastrophes, providing a safer working environment for people working in mines. The advanced rock bolts are embedded with different technologies, such as OMA LWM2M and IPSO Smart Objects, which perform signal processing and detection at high data rates. DarkPulse, a technology-security company, is currently developing an Intelligent rock bolt to assess the health and security of infrastructure for application in mining operations.
Wireless Connectivity for the Connected Mine
Advanced cellular connectivity is the key to ensuring safety in mining operations, enabling IoT use. Smart mines are expected to reduce fatalities by 10% and injuries by 20% over the next decade. However, wired networks have limited accessibility and are susceptible to damage from environmental factors. Besides, short-range solutions such as Wi-Fi are insufficient to deliver the coverage required for reliable signals in hard-to-reach areas. Hence, many mining companies have adopted the third-generation Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) to provide high power and affordable IoT connectivity in remote and complex mining sites. LPWAN nodes can transmit over many kilometers and provide deep penetration capabilities to facilitate IoT in mining. However, the latest enabled private wireless network, 5G, is expected to revolutionize the mining industry, fostering major improvements.
The high bandwidth and low latency offered by 5G can help power complex infrastructure, equipment, and IoT and open up a new level of machine learning and data analytics. With 5G and associated automation, mine operators can reduce accidents and equipment failures resulting from human error, such as truck driver fatigue. NG Mining project commenced by NexGen Mining is a collaboration between Finland’s technical research center VTT, Swedish mining company Sandvik, and Nokia to create a safe and sustainable underground mining through the productive application of autonomous and connected machinery. As the industry digitalizes, the 5G cellular connectivity platform could solve many issues and challenges.
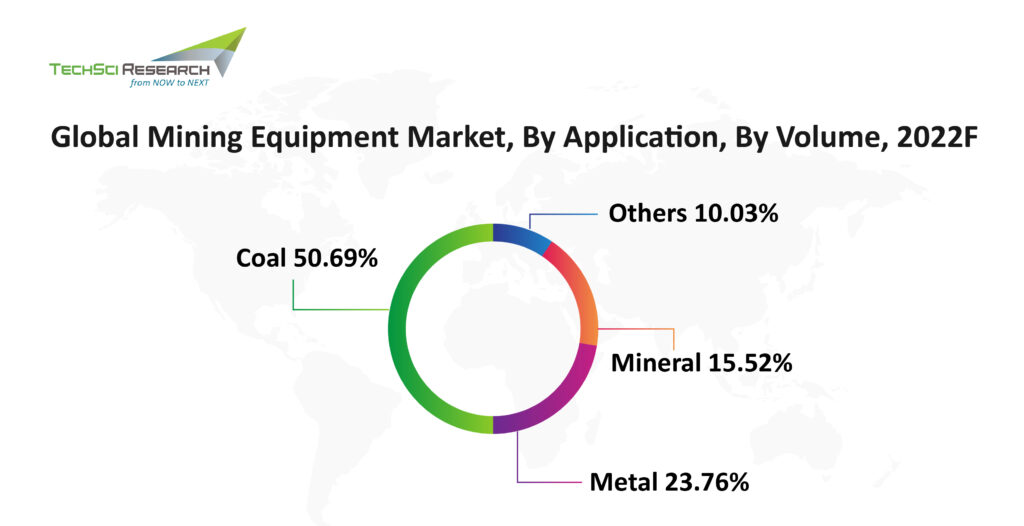
According to TechSci Research report on “Mining Equipment Market – Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Competition, Opportunity and Forecast, 2016-2026 Segmented By Category (Crushing, Pulverizing, Screening, Mineral Processing, Surface & Underground), By Application (Metal, Mineral, Coal, Others), By Propulsion (Diesel, CNG/LNG, Electric), By Power Output (<500HP, 500HP-2000HP, >2000HP), By Vehicle Type (Articulated Dump Trucks, Crawler Dozers, Crawler Excavators, Motor Graders, Rigid Dump Trucks, Drills, Electric Shovels, Hydraulic Excavators, Mining Dozers, Mining Trucks, Wheeled Loaders, Others), By Region”, the global mining equipment industry is expected to reach USD4.5 billion in 2026. The factors attributing to the growth are rising demand for minerals and other materials and expanding digital tools and technologies for mining-related activities.



