Blood Bag Manufacturing in the United States
In the United States, every two seconds someone requires blood either for routine medical procedures or emergency situations. For patients suffering from acute and chronic medical conditions, blood transfusion is an indispensable component of healthcare capable of improving their life expectancy and overall quality of life. Approx. 29000 units of red blood cells, 5000 units of platelets, and 6500 units of plasma are required every day in the United States. According to the American Cancer Society, more than 1.8 million people were diagnosed with cancer in 2020 and required blood during their chemotherapy treatment.
The demand for blood is ever-increasing due to the rising number of accidents and injuries requiring blood transfusion, increasing incidences of severe anemia, expanding diagnostic and treatment options, and the emergence of new medical treatment regimens and procedures. In recent times, blood bag systems have become an indispensable and essential item for hospitals to meet the blood requirements for patients.
Used for collecting plasma and platelets, blood bags act as indispensable components of blood transfusion that maintain sterility of the blood and enhance the reliable collection, separation, storage, and transport of blood. More than 90% of all blood donations are processed through blood bag systems since they allow better separation of blood components in a sterile manner and allow safer transfusion. Blood bags are designed to withstand large temperature variations (–70°C to +120°C) and centrifugation.
Based upon the need for infusion, blood bags can be differentiated into:
Single blood bag
- Designed for whole blood collection
- Contains 63 ml CPDA-1/CPD anticoagulant solution
- Capacity ranges are 250 ml, 350 ml, 450 ml
- It contains a 16G tamper-proof needle and standard donor tubing
Double blood bag
- Designed for separating whole blood into plasma and red cells
- Eliminates the possibility of contamination
- The primary bag contains 63 ml CPDA-1/CPD anticoagulant solution
- 300 ml transfusion bag contains no solution
Triple blood bag for separating packed cells, plasma, and platelets
Quadruple blood bag for separating packed cells, plasma, platelets, and cryoprecipitate
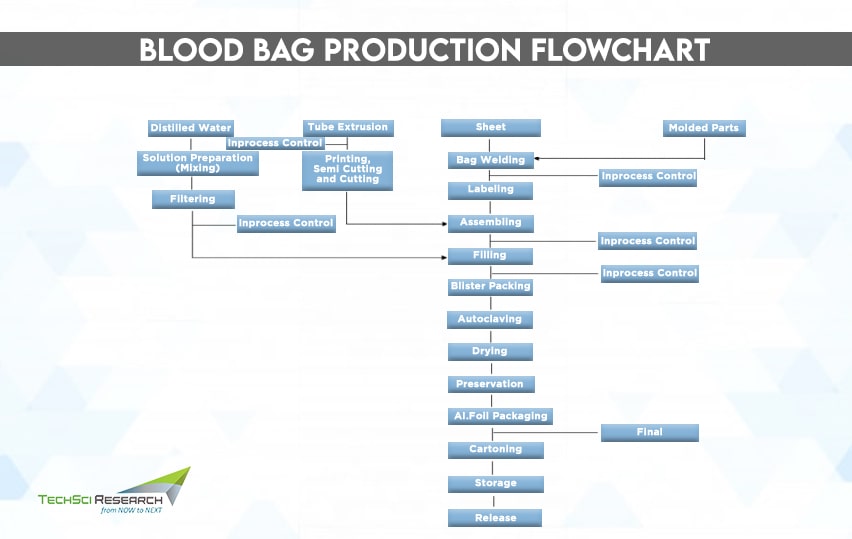
Generally, a blood bag system consists of a collection tube, needle, needle cover, and clamp. Blood bag systems have largely replaced the use of glass bottles since they require thorough cleaning, rinsing, and autoclaving procedures and are vulnerable to breakage during transportation. Besides, air bubbles in glass bottles could lead to severe complications during a blood transfusion. On the contrary, blood bags are made from plastic, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or other materials compatible with blood to reduce the risk of contamination. Unlike glass bottles, blood bags contain anticoagulant and red blood cell preservative solutions to maintain effectiveness.
Medical and surgical manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing items for single-use applications. The main reason for this development is infection control. ‘One-time use’ items like disposable blood bags eliminate the risk of transmission of infectious agents to subsequent patients. Besides, the demand for blood bags is growing due to the hygienic methods adopted for their manufacturing.
Manufacturing of Blood Bag Systems
- Compounding
Polymers are of little value unless compounded with additives such as plasticizers, stabilizers, lubricants, etc., to make useful materials like plastic. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a commonly used material for manufacturing blood bags. Since PVCs are hard and rigid, they are plasticized to provide flexibility to the bags and tubes.
- Extrusion
The plasticized material is extruded through a die to convert it into a sheet form. The extruded sheet is then cut into desired size and shape and welded to form donor and transfer tubing. The tubes are then further printed and cut into appropriate lengths.
- Injection Molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process to produce components like transfusion port, needle cover, clamp, etc., by injecting molten materials into a mold. The manufactured components are then sterilized with ultraviolet light, dried in a drying oven, and cooled. Further, the needle is fixed into the needle holder.
- Welding
High-frequency welding is used to fabricate blood bags by placing PVC sheets between electrodes and applying high voltage simultaneously. Further, transfusion ports, donor, and transfer tubing are organized in inappropriate positions regarding the bag. The welded bags are then trimmed, clamps and needle coverings are fixed on the tubing, and sent to the labelling section.
- Preparation of Anticoagulant Solution
Blood bags are filled with anticoagulants to reduce or extend the blood clotting time period. Acid citrate dextrose is a popular anticoagulant employed in blood bags to inhibit the binding of calcium ions binding in the blood. The constituents of anticoagulants are pre-mixed, and the solution is filled in the blood bags in pyrogen-free distilled water.
- Sterilization
Blood bags are sterilized with autoclaves, in which sterilizing medium is a mixture of steam and air. One of the counterpressure types of sterilization, known as ‘air-over-steam,’ allows control of sterilization pressure independently of the temperature.
- Final Visual Inspection Stage
This step involves eliminating particulate matter, leaks, and other visible defects. All the relevant details regarding the blood bag are thoroughly investigated. The blood bag should not contain any water vapor content to avoid anticoagulant adulteration, the needle should not be bend, and there must be a needle protector with the bag. The bags are subsequently packed and sent into the packing section to ensure quality.
Blood and blood components are always vulnerable to infectious agents as biological fluids. The Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) develops and ensures quality standards related to products such as blood cell separation devices and blood collection containers to maintain blood supply safety. The US Food and Drug Administration has also strengthened its oversight of the blood industry to reduce the risk of contamination to the lowest level without decreasing availability of life-saving resources.
Now the blood establishments must transport and distribute blood and blood components at all stages of transfusion to maintain the quality of the product. As per the FDA regulation, a blood bag not containing anticoagulant solution is treated as a device, whereas a blood bag with the solution is treated as a drug-device combination product but still regulated as a drug.
How Blood Bag System Collects Blood?
The whole blood collection set consists of the main donor bag with blood and small plastic bags attached, which may be empty or full of nutrient fluid. The healthcare provider places the product code label on the blood bag to indicate the components in which the plasma should be segmented. Then the technician places the whole blood in a centrifuge cup and then into the floor model centrifuge, which is the size of the washing machine.
Then the blood spins and separates, where RBCs reach the bottom of the donation bag, whereas plasma floats on top. After the centrifuge stops spinning, the whole blood is removed and placed in a machine that pushes the plasma out in one of the attached bags. Then, the nutrient fluid stored in one of the attached bags is combined with RBCs to last longer in the refrigerator. Then, white blood cells are filtered out from the red blood cells floating in the nutrient-dense fluid. While RBCs are placed in the fridge for future patient transfusion, the plasma product is frozen and placed in a big freezer.
Role of RFID Technologies to Reduce Blood Transfusion Errors
Blood transfusion errors have remained a common occurrence at medical facilities due to mishandling or other kind of manual interventions. However, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technologies can help address human and systems errors in the blood transfusion supply chain and ensure safe blood delivery.
RFID integrated blood bags reduce the chances of errors and make transfusion processes more robust. Besides, modern technology plays an important role in generating logistic and temperature data of blood products, which would be essential for optimizing the quality of the blood transfusion chain. RFID is considered a more advanced and effective technique than barcode to generate accurate data.
Way Ahead
Leading manufacturers like Terumo BCT, Fresenius Kabi, Macopharma, and others are introducing a comprehensive range of customized blood bags in hospitals and transfusion centers to fulfill the demand for customized blood bags in platelets and plasma collection procedures. Besides, there has been increasing use of biodegradable thermoplastic polyurethane for making blood bags to reduce plastic pollution caused by PVC plastic bags. With continuous developments in blood collection technology and rising incidences of blood-related disorders, the blood bag market is anticipated to grow further in the coming years.
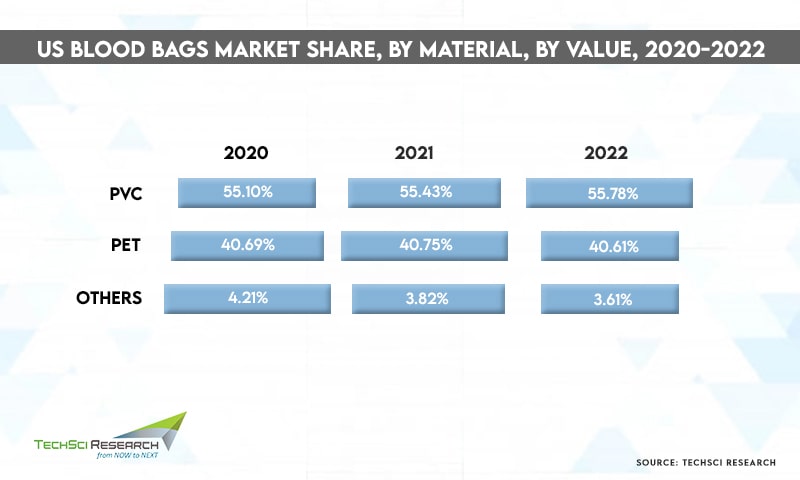
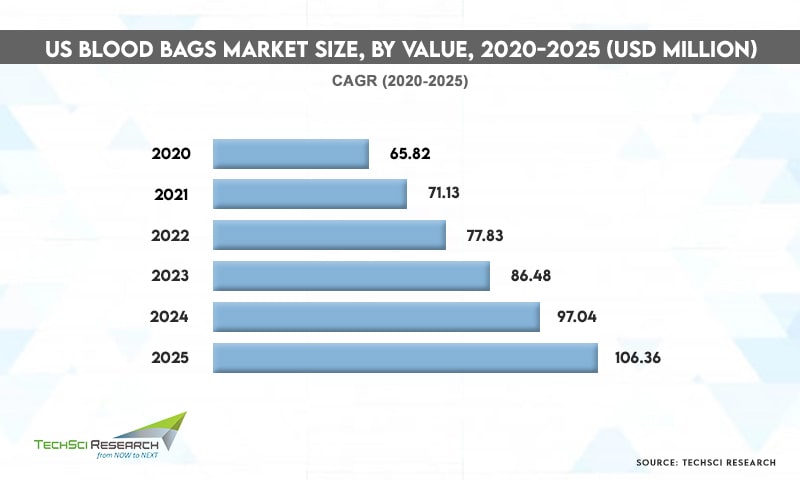
According to TechSci Research report “United States Blood Bags Market By Product Type (Single Blood Bag, Double Blood Bag, Triple Blood Bag, Quadruple Blood Bag, Penta Blood Bag) By Type (Collection Bag v/s Transfer Bag) By Volume (100ml, 150ml, 250ml, 300ml, 350ml, 400ml, 450ml, 500ml) By Material (PVC, PET, Others) By End User (Hospitals, Clinics, Ambulatory Surgical Center, Blood Banks, Others) By Company, By Region, Forecast & Opportunities, 2026”, the United States blood bags market is expected to grow at a significant rate owing to the rise in government initiatives to promote blood donations. Besides, rising incidences of chronic disorders and high occurrence of trauma and injuries are contributing to the growth of the United States blood bags market.